Integrated & reliable
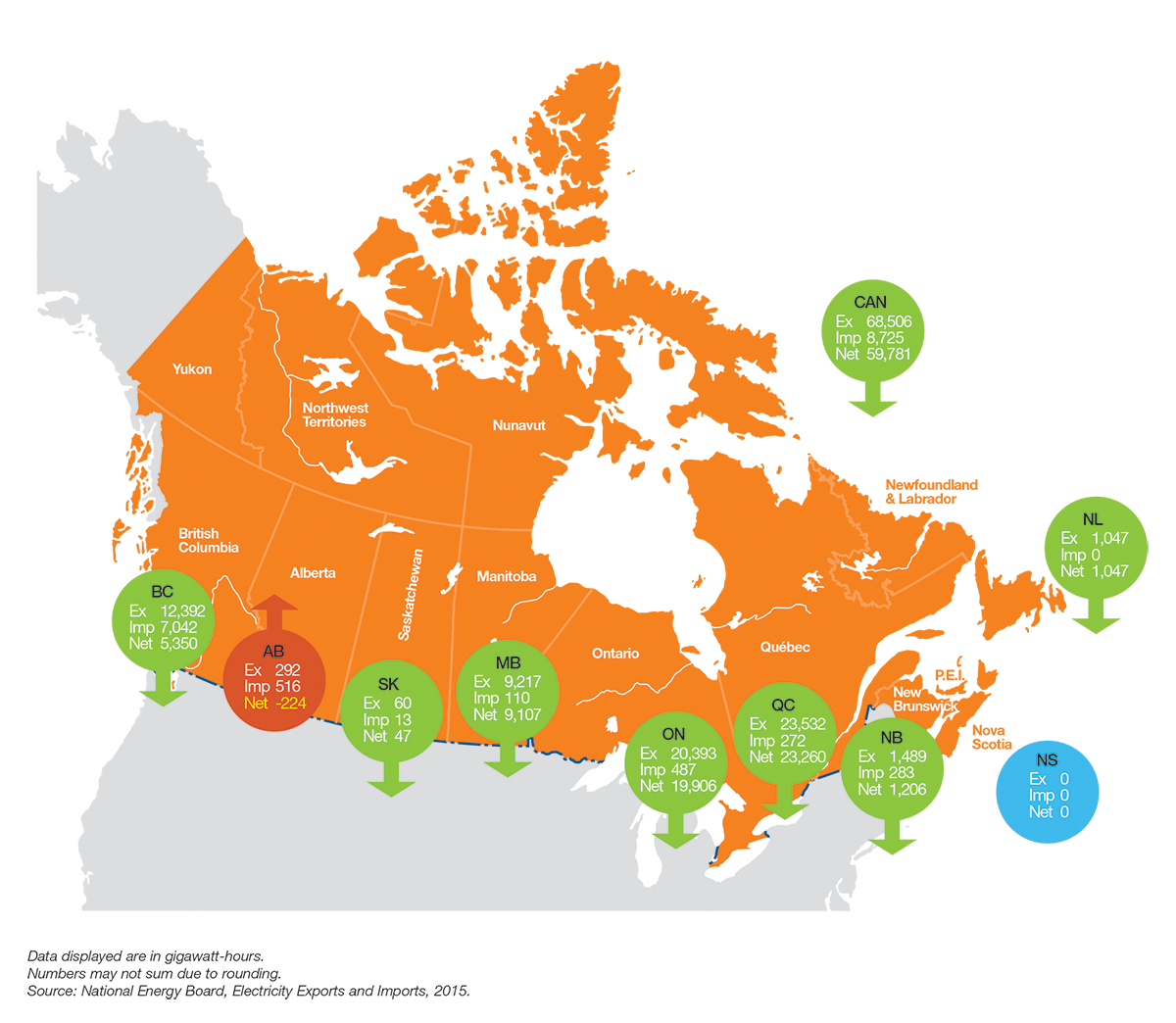
The U.S. and Canada are each other’s largest trading partners – and in no area more crucial than energy. The electricity grids of our two countries are highly interconnected – in fact, they represent a single North American grid, composed of over 200,000 miles of high-voltage transmission lines and 35 interconnections. In 2019, 73.8 million megawatt-hours (MWh) of electrical energy flowed across the U.S.–Canada border in both directions.
Regional benefits of our electricity trade include:
- Lower rates
Hydropower helps stabilize electricity prices in regions subject to the price volatility inherent in fossil fuels. See Energy security. - Better air quality
Renewable, clean hydropower displaces the release of greenhouse gases and pollutants from fossil fuel-burning non-renewable energy sources. See Reducing emissions. - Improved regional reliability
Fast-ramping hydropower can almost instantaneously respond to fluctuations in supply and demand, helping to avoid system failures during emergencies and rapidly re-establishing system operation in the event of a blackout. - Reduced capital investment
Utilities with different seasonal demands for energy share generation capacity (for example, U.S. demand peaks in summer with air conditioning load; Manitoba demand peaks in winter for heating). A more efficient use of regional energy supply reduces the need to build new costly power plants. - More efficient operations
Cooperation between utilities allows system operators to take advantage of a wide spectrum of resources over a large area, reducing variability in generation and demand and mitigating price volatility. - Better for the environment
North American governments are in agreement that increased international trade in clean, renewable electricity is a key factor in addressing climate change.
Shared market practices
Cross-border electricity trade between the U.S. and Canada is made possible by adherence to a common set of operational and commercial rules.
Compliance with these terms ensures a greater diversity of cost-competitive supply options for customers throughout North America.
- To ensure a seamless flow of electrons across our shared border, both countries participate in the standard market practices and protocols utilized by Independent System Operators (ISOs), Regional Transmission Organizations and other market participants.
- Manitoba Hydro is a coordinating member of the U.S.-based Midcontinent Independent System Operator (MISO).
- The U.S. and Canada adhere to electric reliability standards developed by the North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC), which are mandatory and enforceable in all Canadian provinces with a footprint in the North American bulk power system.
- Renewable energy tracking systems have been used successfully for decades to track trade and retire Renewable Energy Credits (RECs) in relation to various state and voluntary energy commitments.